Hypertension
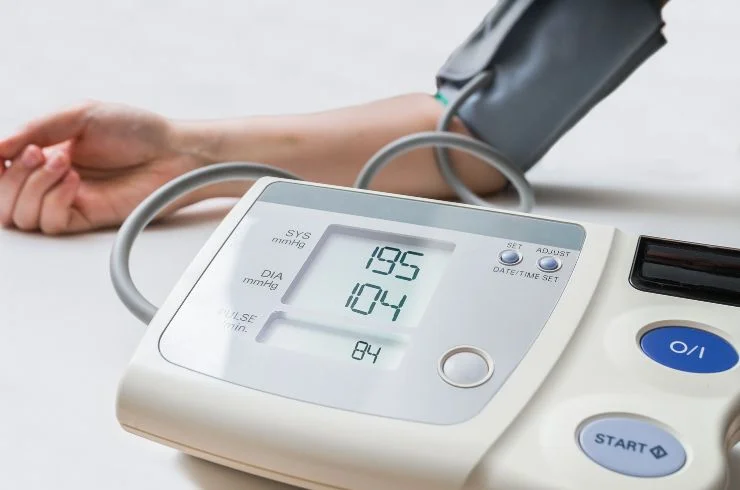
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a condition where the force of the blood against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high. Blood pressure is measured using two numbers: systolic pressure (the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats) over diastolic pressure (the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats). A normal blood pressure reading is usually around 120/80 mmHg. When your blood pressure consistently reads at or above 130/80 mmHg, it is considered hypertension. This condition often has no symptoms, which is why it’s often referred to as the “silent killer.”
Managing hypertension is crucial because if left untreated, it can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney damage, and other serious conditions.
Factors that contribute to high blood pressure include obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, excessive salt intake, stress, alcohol consumption, and a family history of hypertension. Regular monitoring of your blood pressure is essential, especially if you have risk factors. Keeping a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and stress management, can significantly lower your risk of developing high blood pressure.
If you are diagnosed with hypertension, your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medications to help control your blood pressure. Lifestyle changes can include reducing your salt intake, eating more fruits and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and limiting alcohol consumption. It’s important to follow your doctor’s advice and attend regular check-ups to monitor your blood pressure and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. By actively managing your blood pressure, you can reduce your risk of serious health issues and maintain a healthier lifestyle.