Diabetes
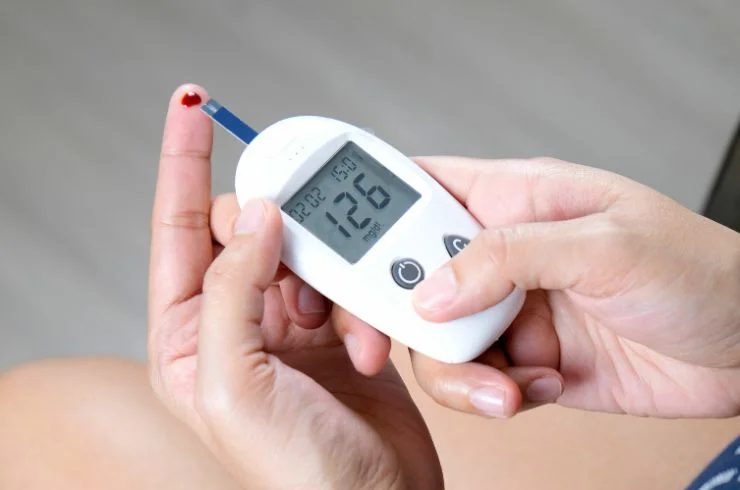
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that occurs when the body cannot properly regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels. There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. In Type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to little or no insulin production. This type often develops in childhood or adolescence. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is more common and typically develops in adults, although it can occur in children. In this type, the body either becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. High blood sugar can lead to serious health complications if not managed effectively.
The symptoms of diabetes can vary but often include increased thirst, frequent urination, extreme fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of wounds.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis. Regular blood sugar monitoring is vital for individuals with diabetes, as it helps to maintain glucose levels within a target range. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems.
Managing diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and possibly medication. A healthy diet that emphasizes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats is crucial. Engaging in regular physical activity can also help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Additionally, following your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding medications, insulin therapy, and routine check-ups will help you manage your condition effectively. By actively participating in your diabetes management plan, you can lead a healthy and fulfilling life while minimizing the risks associated with the disease.